1. A pitot tube is used to measure
a) pressure
b) difference in pressure
c) velocity of flow
d) none of these.
a) pressure
b) difference in pressure
c) velocity of flow
d) none of these.
a) one-third of the height of water on the sill
b) one-half of the height of water on the sill
c) one-fourth of the height of water on the sill
d) none of these.
a) ψ is constant everwhere on any stream line
b) the flow around any path in the fluid is zero for continuous flow
c) the rate of change of ψ with distance in an arbitrary direction, is proportional to the component of velocity normal to that direction
d) all the above.
a) 2.7 m of water
b) 7.4 m of water
c) 5.5 m of water
d) none.
a) 1 metre of water
b) 2 metres of water
c) 3 metres of water
d) 4.0 metres of water.
a) area is horizontal
b) area is vertical
c) area is inclined
d) all the above.
a) specific weight
b) specific mass
c) specific gravity
d) none of these.
a) fluid is non-viscous
b) fluid is homogeneous
c) flow is steady
d) all the above.
a) (2L/C)
b) less than or equal to (2L/C)
c) greater than (2L/C)
d) less than (4L/C)
a) to connect water reservoirs at different levels intervened by a hill
b) to supply water to a town from higher level to lower level
c) to fill up a tank with water at higher level from a lower level
d) none of these.
a) depth of water = 0.95 diameter of circular section
b) hydraulic mean depth = 0.286 diameter of circular section
c) wetted perimeter = 2.6 diameter of circular section
d) all the above.
a) m2/sec
b) Newton sec/m2
c) Newton sec/m3
d) Kg sec/m2.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 
a) 
b) 
c)

d)

a)

b) 
c) 
d) 
a) 0.5
b) 0.75
c) 1.25
d) 2.00
a) maximum at the centre
b) maximum at the inside of surface
c) same throughout the section
d) none of these.
a) 
b) 
c)

d) 
a) 2
b) 3
c) 1/2
d) 1/3
a) 1 to 4
b) 1 to 3
c) 1 to 2
d) 1 : 5

a) 10,000 kgf
b) 15,000 kgf
c) 20,000 kgf
d) 18,000 kgf.
a)
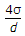
b) 
c) 
d) 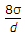
a) 1.25
b) 1.33
c) 1.50
d) 1.66
a) velocity head
b) static pressure
c) total pressure
d) negative static pressure.
a) elevation energy
b) kinetic energy
c) pressure energy
d) none of these.
a) less than 12.2 m of the water
b) more than 12.2 m of the water
c) equal of 12.2 m of water
d) none of these.
a) length
b) depth
c) shape
d) both (b) and (c).
a) 2/g m of water
b) g/2 m of water
c) 1g m of water
d) (sqrt g) m of water.
a) 25%
b) 33.3%
c) 50%
d) 66.67%.
a) Continuity equation
b) Newton's law of viscosity
c) Newton's second law of motion
d) dynamic viscosity law,
a) 
b)

c) 
d) ρdp + gdz + vdv = 0
a) viscosity
b) elasticity
c) gravitational force
d) surface tension.
a) weight of the body
b) weight of the fluid displaced by the body
c) weight of the body and fluild displaced by the body
d) none of these.
a)

b)

c) 
d) none of these.
a) 400 H.P.
b) 450 H.P.
c) 500 H.P.
d) 550 H.P.
a) water hammer
b) hydraulic jump
c) critical discharge
d) none of these.
a)

b) 
c)

d) none of these.
a) weight of liquid vertically below the curved surface
b) force on a vetical projection of the curved surface
c) product of pressure at its centroid and the area
d) weight of liquid retained by the curved area.
a) π
b) 2π
c) 3π
d) 4π
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 
a)

b)

c) 
d)

a) pressure in water channels, pipes, etc.
b) difference in pressure at two points
c) atmospheric pressure
d) very low pressure.
a) cannot be compressed
b) do not occupy definite shape
c) are not affected by change in pressure and temperature
d) none of these.
a) 2/3
b) 3/2
c) 2/5
d) 5/2
a) Euler number
b) Frode number
c) Reynold number
d) Weber number.
a) hydraulic mean depth = 1.5 m
b) Velocity of flow = 1.5 m/sec
c) Rate of flow = 27 m3/sec
d) All the above.
a) Bhakra dam
b) Hirakund dam
c) Nagarjuna Sagar dam
d) Idukki dam.
a) half of the top width must be equal to one of the sloping sides
b) the hydraulic mean depth must be equal to half the depth of flow
c) the semicircle drawn with top width as diameter must touch the three sides of the channel
d) All of these.
a) for lifting water without an electric motor
b) for accelerating water flow
c) for lifting heavy loads
d) none of these.
a) absolute pressure - atmospheric pressure
b) absolute pressure + atmospheric pressure
c) atmospheric pressure - absolute pressure
d) none of these.

a) Internal mouth piece
b) Re-entrant mouth piece
c) Borda's mouth piece
d) All the above.
a)

b) 
c) 
d) none of these.
a) 0.25 s
b) 0.50 s
c) 1.0 s
d) 1.5 s.
a) 2 m
b) 2.5 m
c) 3.0 m
d) 4.0 m.
a) higher than the surface of liquid
b) same as the surface of liquid
c) lower than the surface of liquid
d) none of these.
a) expresses the relationship between work and energy
b) relates the momentum per unit volume between two points on a stream line
c) relates mass rate of flow along a stream line
d) requires that Newton's second law of motion be satisfied at every point in fluid.
a) 17.5 m3
b) 20.0 m3
c) 22.5 m3
d) 25 km3.
a) to relieve the pressure due to water hammer
b) to provide additional water head
c) to overflow the pipe line when suddenly closed
d) to remove the frictional loss in pipe.
a) potential head and kinetic head
b) potential head and kinetic head
c) potential head and pressure head
d) potential head, kinetic head and pressure head.
a) hyperbolic
b) circular
c) parabolic
d) elliptical.
a) its vaour pressure is practically zero
b) the height of the barometer will be less
c) it is a best liquid
d) both (a) and (b) above
a) less than 2100
b) more than 3000
c) between 2100 and 3000
d) none of these.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d)

a) potential energy
b) kinetic energy
c) pressure energy
d) all the above.
a) fluid is viscous
b) fluid is homogeneous and incompressible
c) velocity of flow is non-uniform over the section
d) flow is unsteady along the stream line.
a) 31.1 m/sec
b) 31.2 m/sec
c) 31.3 m/sec
d) 31.4 m/sec.
a) a long pipe at decreasing rate
b) a long pipe at constant rate
c) an expanding tube at constant rate
d) an expanding tube at increasing rate
a) Low pressure
b) High pressure
c) Low velocity
d) None of these.
a) viscosity
b) surface tension
c) gravitational force
d) elasticity.
a)

b) 
c) 
d) 
a) The velocity of energy of liquid particle, across any cross-section of a pipe is uniform
b) No external force except the gravity acts on the liquid
c) There is no loss of energy of the liquid while flowing
d) All the above.
a) 
b)

c) 
d) 
a) 
b) 
c) 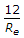
d) 
a) 
b) 
c)

d) none of these.
a) minimum
b) maximum
c) average of maximum and minimum
d) None of these.
a) Reynold number
b) Froude number
c) Weber number
d) Mach number.
a) 2.0 m3
b) 2.5 m3
c) 3.0 m3
d) 4.0 m3
a) minimum
b) maximum
c) equal throughout
d) none of these.
a) increases
b) decreases
c) remains unaffected
d) None of these.
a) 2 mm
b) 4 mm
c) 6 mm
d) 8 mm
a) increases the discharge
b) decreases the discharge
c) does not effect the discharge
d) none of these.
a) pressure in water channels, pipes etc.
b) difference in pressure at two points
c) atmospheric pressure
d) very low pressure
a) one-fourth of the width
b) three times the hydraulic radius
c) half the width
d) none of these.
a) rectilinear flow
b) radial flow
c) free vortex motion
d) forced vertex.
a) conditions of flow change steadily with time
b) conditions of flow do not change with time at a point
c) conditions of flow remain the same at adjacent point
d) velocity vector remains constant at a point.

a) 14,137 kgf
b) 5,863 kgf
c) 20,000 kgf
d) 18,000 kgf.
a) a straight line
b) a circular path
c) an elliptical path
d) a parabolic path.
a) 2°
b) 3°
c) 4°
d) 5°
a) (H2 - H1 ) > H
b) (H2 - H1 ) > H/4
c) (H2 - H1 ) > H/2
d) (H2 - H1 ) > H/3
a) 459 kg
b) 549 kg
c) 945 kg
d) 954 kg