1. In case of Raymond pile
a) lengths vary from 6 m to 12 m
b) diameter of top of piles varies from 40 cm to 60 cm
c) diameter of pile at bottom varies from 20 cm to 28 cm
d) all the above.
a) lengths vary from 6 m to 12 m
b) diameter of top of piles varies from 40 cm to 60 cm
c) diameter of pile at bottom varies from 20 cm to 28 cm
d) all the above.
a) in header course
b) in stretcher course
c) in header course next to first brick
d) in stretcher course next to first brick
a) dinning halls
b) bath rooms
c) living rooms
d) verandah
a) strip footing
b) strap footing
c) combined footing
d) none of these.
a) strength
b) workability
c) stability of structure
d) all the above.
a) are vertical wooden members
b) is the upper horizontal wooden member
c) is the lower horizontal wooden member
d) are the intermediate horizontal wooden members.
a) inclined borings are made for taking samples under existing structures
b) inclined borings are occasionally used instead of vertical holes.
c) the spacing of inclined borings is kept such that one bore hole is vertically above the bottom of an adjacent bore hole.
d) all the above.
a) the seisomic method
b) electrical resistivity method
c) gravitational method
d) both (a) and (b) of the above.
a) at the centre of the base
b) within the middle third of the base
c) within the middle fifth of the base
d) neither (a), (b) nor (c).
a) stretcher
b) face
c) front
d) header
a) 1 cm per metre length
b) 2 cm per metre length
c) 4 cm per metre length
d) 5 cm per metre length.
a) soffit
b) intrados
c) haunch
d) back
a) 5 to 10 cm
b) 15 to 20 cm
c) 25 to 30 cm
d) 30 to 45 cm
a) dubbing
b) hacking
c) blistering
d) peeling.
a) bearing capacity is low
b) permeability is uncertain
c) particles are cohesive
d) property to undergo a volumetric change due to variation of moisture content.
a) the column spacing
b) one-third the column spacing
c) half the column spacing
d) none of these.
a) closer
b) half brick
c) bed
d) bat.
a) 25 to 50 mm
b) 25 to 75 mm
c) 30 to 125 mm
d) none of these.
a) purlin
b) cleat
c) batten
d) strut
a) Louvered door is generally provided in bath rooms
b) Flush door is generally provided in dinning room
c) Revolving door is generally provided in cinema halls
d) All the above.
a) is used to transfer heavy structural loads from steel columns to a soil having low bearing capacity
b) is light and economical
c) does not require deep cutting as the required base area with required pressure intensity is obtained at a shallow depth
d) all the above.
a) turn
b) junction
c) quion
d) all the above.
a) 1/6th of the span
b) 1/8th of the span
c) 1/10th of the span
d) 1/12th of the span
a) 350
b) 420
c) 450
d) 500
a) a base course is prepared as in cement concrete flooring
b) a 32 mm thick layer of cement concrete (1 : 2 : 4) is laid on the base course and the surface is made smooth by trowelling
c) glass strips are driven into the layer according to the pattern required
d) none of these.
a) heat insulated
b) sound insulated
c) neither (a) nor (b)
d) both (a) and (b).
a) Simplex pile
b) Mac-Arthur pile
c) Raymond pile
d) none of these.
a) sides of beams and girders
b) column forms
c) bottom of beams and girders
d) all the above at the same time.
1. ramming the foundation bed
2. excavation of the soil upto required depth
3. laying the reinforcement over the foundation bed
4. curing the cement concrete placed over reinforcement
5. pouring the cement concrete over the reinforcement.
The correct sequence is
a) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
b) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
c) 2, 1, 3, 5, 4
d) 3, 2, 5, 1, 4.
a) L/100
b) L/150
c) L/360
d) none of these.
a) round steps
b) angular steps
c) winders
d) radial steps
a) ground water observations are hindered due to entry of the slurry in the soil below the bottom of the hole
b) caving or mixing of strata are caused in soft soils or cohesionless soils
c) the soil to a considerable depth below the bottom of the hole gets disturbed
d) all the above.
a) one course of headers to three or five course of stretchers
b) queen closer in provided in each heading course
c) the middle course of stretchers is started with a header to give proper vertical joints
d) all the above.
a) cornice
b) coping
c) frieze
d) lintal.
a) ridge
b) hip
c) valley
d) none of these.
a) auger boring
b) percussion drilling
c) diamond drilling
d) wash boring.
a) 5 m
b) 10 m
c) 15 m
d) 20 m
a) queen closer
b) bevelled closer
c) king closer
d) half king closer.
a) header
b) stretcher
c) closer
d) none of these.
a) cleat
b) stop
c) horn
d) none of these.
a) The function of foundation is to distribute the load of super structure over a large bearing area
b) No timbering is required for shallow trenches
c) Shallow foundations can be constructed on made-up soil
d) Black cotton soil is very good for foundation bed.
a) 2 cm
b) 4 cm
c) 6 cm
d) 8 cm
a) the direction of the prevailing winds in the area
b) the exposure of the walls and roof of the buildings to the rays of sun
c) the extent up to which the sunrays penetrate with the verandah.
d) all the above.
a) Cement is added to lime mortar to increase its hydraulic properties only
b) Lime surkhi mortar is used for pointing the walls
c) Lime should be slaked before preparing lime mortar
d) High early strength concrete is generally used in cold weather.
a) granite
b) marble
c) sand stone
d) slate
a) in soils that require lateral support
b) in cohesive soils
c) in soft soils
d) none of the above.
a) 1 day
b) 4 days
c) 7 days
d) 14 days.
a) two curved arches
b) gothic arches
c) ogee arches
d) drop gothic arches.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d)

a) 
b) 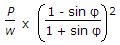
c) 
d) 
a) are suitable for works under sea water
b) resist shocks or vibrations
c) are suitable for use as batter piles
d) are useful for heavy vertical loads.
a) ground level and springing line
b) crown and springing line
c) crown and ground level
d) intrados and extrados.
a) 10 m
b) 20 m
c) 30 m
d) 40 m
a) platform
b) relief
c) rest
d) landing
a) 25% to total area
b) 30% of total area
c) 40% to total area
d) 50% of total area.
a) mansored truss
b) queen post truss
c) king post truss
d) none of these.
a) The retaining wall should be structurally capable to resist the applied earth pressure
b) The section of the retaining wall should be so proportioned that it may not overturn by the lateral pressure
c) The retaining wall should be safe against sliding
d) to drain off water from the earth retained, weep holes are provided near the top of the retaining wall.
a) shoring
b) underpinning
c) jacking
d) piling
a) finishing of concrete
b) curing of concrete
c) placing of concrete
d) none of these.
a) skew back
b) soffit
c) spandril
d) haunch
a) 20 tonnes/m2
b) 40 tonnes/m2
c) 50 tonnes/m2
d) 60 tonnes/m2
a) 9 cm x 9 cm x 9 cm
b) 9 cm x 9 cm x 4.5 cm
c) 9 cm x 4.5 cm x 9 cm
d) 1.8 cm x 4.5 cm x 9 cm.
a) 15 mm
b) 25 mm
c) 35 mm
d) 45 mm
a) h/4
b) 1/2 h
c) h
d) 2 h.
a) The lowest layer consists of consolidated ground
b) A 10 cm thick clean sand is laid on consolidated ground
c) A 10 cm lime concrete (1 : 4 : 8) is laid on clean sand
d) A 10 cm thick cement concrete (1 : 2 : 4) is laid on top layer.
a) is not suitable for deposits containing very coarse gravel
b) hinders the ground water observations and permeability test
c) is not economical for holes of less than 10 cm.
d) all the above.
a) vibro pile
b) pressure pile
c) Franki pile
d) pedestal pile.
a) upper flange of top tier
b) lower beam of lower tier
c) ends of external beams
d) none to these.
a) ceiling
b) 15 cm above floor level
c) 200 cm
d) level of the tap.
a) black cotton soil
b) loose fine sandy soil
c) dry coarse sandy soil
d) hard rocks
a) dead loads
b) live loads
c) wind loads
d) all of these.
a) undergoes volumetric changes
b) swells excessively when wet
c) shrinks excessively when dry
d) all the above.
a) In dog-legged stairs, no space between its flights is provided
b) In open newel stair, a rectangular well is provided
c) In geometric stair, a curved shaped well between forward and backward flights, is provided
d) In geometrical stair, two quarter space landing is provided.
a) jambs
b) lintels
c) reveals
d) soffits.
a) first class bricks are used
b) vertical joints in alternate courses are kept in plumb line
c) bats are used where necessary
d) all the above.
a) providing increased area of foundation over poor bearing capacity of soil
b) spanning over small soft or loose pockets
c) counter acting the hydrostatic effect
d) all the above.
a) 1:1
b) 1:2
c) 1:3
d) 1:4
a) ashlar arch
b) rubble arch
c) gauged arch
d) axed arch.
a) heat insulation
b) sound insulation
c) prevention of dampness
d) all the above.
a) efflorescence
b) bleaching of paints
c) crumbling of plaster
d) All of these.
a) combined footing
b) strap footing
c) raft footing
d) none of these.
a) draining sub-soil water
b) ramming crushed stone in soil
c) watering surface of soil
d) none of these.
a) combined footing
b) raft footing
c) pier footing
d) none of these.
a) mosaic floor
b) terrazo floor
c) chips floor
d) marble floor.
a) brick on edge
b) brick on end
c) brick on bed
d) brick held vertically.
a) English bond
b) stretcher bond
c) header bond
d) single Flemish bond.
a) stretcher
b) face
c) front
d) header
a) looking through the well in the vicinity
b) standing on the well in the vicinity
c) measuring the depth of water in the well
d) none of the above.
a) the pile driven in sand is called sand pile
b) the drilled hole filled with sand is called sand pile
c) the sand piles are used for bearing purposes
d) None of these.
a) the cost of square rooms is less
b) the expenditure on the foundation and roof for the double storeyed building is nearly half of that for the ground storeyed building.
c) the cost of construction of a house may be minimised by restricting the height floors
d) all the above.
a) 10 mm
b) 20 mm
c) 30 mm
d) 40 mm
a) simplex pile
b) Franki pile
c) pressure pile
d) vibro pile.
a) dormer window
b) sky light window
c) lantern window
d) louvered window.
a) chamfered ashlar masonry
b) ashlar facing masonry
c) random coursed ashlar masonry
d) coursed ashlar masonry.
a) spandril
b) haunch
c) springing
d) soffit
a) 0°
b) 30°
c) 60°
d) 90°
a) swelling and shrinkage characteristics prevail
b) consolidation continues even after several years of construction.
c) differential settlement is generally prevalent
d) all the above.
a) the width of the wall is constructed thicker at the base in a stepped fashion
b) a long vertical load transferring concrete structure is called a concrete pile
c) the pile which transfers the load to a hard rock bed at certain depth is called load bearing
d) none of the these.
a) 10 cm
b) 15 cm
c) equal to its projection beyond wall base
d) less than its projection beyond wall base.
a) lean concrete bed is provided
b) thick concrete bed is provided
c) reinforced concrete bed is provided
d) (a) and (c) of the above