1. In a liquid limit test, the moisture content at 10 blows was 70% and that at 100 blows was 20%. The liquid limit of the soil, is
a) 35%
b) 50%
c) 65%
d) none of these.
a) 35%
b) 50%
c) 65%
d) none of these.
a) tan (45° - φ)
b) tan2 (45° + φ/2)
c) tan2 (45° - φ/2)
d) tan (45° + φ)
a) liquid limit
b) plastic limit
c) shrinkage limit
d) permeability limit.
a) The rise of the ground surface due to frost action is called frost heave.
b) The freezing of water is accompained by a volume increase of 9%.
c) Below freezing point, higher soil suction develops.
d) All the above.
a) Clays are more porous than sands
b) Pressure of organic matter in a soil decreases the bearing capacity of the soil
c) Aluminous cement is used for foundations in soils with chemical deposits
d) All the above.
a) is equal to mass of the soil retained
b) proportional to the depth of the soil
c) proportional to the internal friction of the soil
d) none of these.
a) decreases as the moisture content increases
b) increases as the moisture content decreases
c) is more in well compacted clays
d) depends upon the external applied load.
a) coefficient of permeability of soil
b) total head loss through the soil
c) neither (a) nor (b)
d) both (a) and (b).
a) quick test
b) drained test
c) consolidated undrained test
d) none of these.
a) liquid limit
b) plastic limit
c) shrinkage limit
d) permeability limit.
a) 0.002 mm
b) 0.04 mm
c) 0.06 mm.
d) 0.08 mm
a) less than 1
b) 1
c) more than 1
d) None of these.
a)

b) 
c) 
d) 
a) 
b) 
c)

d) 
a) driven piles
b) bored piles
c) precast piles
d) all the above.
a) Kaolinite group
b) Illite group
c) Vermiculite group
d) Montrorillonite group.
a) actual cohesion to that required to maintain stability of slope
b) shear strength to shear stress along the surface
c) neither (a) nor (b)
d) both (a) and (b).
a) porosity
b) specific gravity
c) void ratio
d) water content.
a) 11.1%
b) 55.6%
c) 69.6%
d) none of these.
a) 20%
b) 77%
c) 92%
d) none of these.
a) 
b) 
c)

d) 
a) down and outwards on a slip surface
b) up and inwards on a slip surface
c) horizontal upward and parallel to base
d) horizontal inward and parallel to base.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 
a) D10
b) D20
c) D30
d) D60
a) 50%
b) 60%
c) 75%
d) 80%
a) stress to strain
b) strain to stress
c) stress to settlement
d) rate of loading to that of settlement.
a) slope failure
b) face failure
c) base failure
d) toe failure.
a) soil mass is homogeneous, dry and cohesionless
b) ground surface is a plane which may be horizontal or inclined
c) back of the wall is vertical and smooth
d) all the above.
a) volume of water to volume of given soil
b) volume of water to volume of voids in soil
c) weight of water to weight of air in voids
d) weight of water to weight of solids of given mass of soil.
a) calcium carbide method
b) sand bath method
c) alcohol method
d) oven-drying method.
a) shape of grain
b) weight of grain
c) size of grain
d) shape, size and weight of grain.
a) When water table is above the base of a footing, the dry weight m should be used for soil below water table
b) When water table is located somewhat below the base of a footing, the elastic wedge is partly of moist soil and partly of submerged soil, and a suitable reduction factor is used
c) When water table is just at the base of the footing, no reduction factor is used
d) None of these.
a) In soils, the flow index indicates variation in shear strength with water content
b) Liquid limit minus plastic limit, is known as plasticity index of the soil
c) Plastic limit minus shrinkage limit, is known as shrinkage index of the soil
d) All the above.
a)

b)

c)

d) none of these.
a) sandy soils
b) silty soils
c) gravel soils
d) clay soils.
a) H/4 above the base parallel to base
b) H/2 above the base parallel to base
c) H/3 above the base parallel to base
d) H/5 above the base parallel to base.
a) porosity
b) specific gravity
c) void ratio
d) water content.
a) depth of the compressible soil strata
b) compressive index
c) both (a) and (b)
d) none of these.
a) perpendicular to the equipotential lines
b) proportional to the exit graident
c) proportional to the head loss
d) all the above.
a) 1.0 g/cm2
b) 1.5 g/cm3
c) 2.0 g/cm3
d) 2.5 g/cm3
a) Sandy clayloam contains highest percentage of sand
b) Silty clayloam contains highest percentage of silt
c) Soft chalk carries least safe load
d) All the above.
a) Kaolinites .
b) Montomorillonite
c) Illites
d) All the above.
a) plastic limit minus the natural water content, to its plasticity index
b) natural water content minus its plastic limit to its plasticity index
c) natural water content plus its plastic limit to its plasticity index
d) liquid limit minus the natural water content to the plasticity index.
a) cement and water mix
b) clay suspension
c) sodium silicate
d) all the above.
a) 0.25
b) 0.50
c) 0.75
d) 1.00
a) slip plane
b) a horizontal surface
c) a curved surface
d) all the surfaces.
a) Failure plane carries maximum shear stress
b) Failure plane does not carry maximum shear stress
c) Failure plane carries shear stress equal to maximum shear stress
d) None of these.
a) Upheavel → transportation → deposition → weathering
b) Weathering → upheaval → transportation → deposition
c) Weathering → transportation → deposition → upheaval
d) None of these.
a) 5%
b) 10%
c) 15%
d) 20%
a) 30°
b) 45°
c) 60°
d) 90°
a) 15%
b) 18%
c) 20%
d) 25%
a) multiplied by unit weight of water
b) divided by unit weight of water
c) plus unit weight of water
d) minus unit weight of water.
a) An unconfined compression test is a special case of triaxial compression test
b) An unconfined compression test is a special case of direct shear test
c) The confining pressure is maximum during an unconfined compression test
d) The cylindrical specimen of a soil is subjected to major principal stress till it fails due to shearing along the plane of the failure.
a) one phase soil
b) two phase soil
c) three phase soil
d) four phase soil.
a) swell more when wet
b) shrink more when dry
c) possess high coefficient of internal coefficient
d) None of these.
a) 2.0
b) 2.25
c) 2.50
d) 2.75
a) Kaolinite is most stable clay
b) Kaolinite shows a very little sign of swelling on wetting
c) Kaolinite when wet, becomes moderately plastic because negative electro magnetic charges on platelets attrack water
d) All the above.
a) 100 tonnes
b) 50 tonnes
c) 20 tonnes
d) 10 tonnes.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d)

a) To an agriculturist, soil is the substance existing on the earth's surface, which grows and develops plants
b) To a geologist, soil is the material in a relatively thin surface zone within which roots occur, and rest of the crust is termed as rock irrespective of hardness
c) To an engineer, soil is the unaggregated and uncemented deposits of minerals and organic particles covering the earth's crust
d) All the above.
a) co-efficient of consolidation
b) degree of consolidation
c) consolidation index
d) consolidation of undisturbed soil.
a) sandy soils
b) cohesive soils
c) stratified soils
d) clayey soils.
a) 
b) 
c)

d) 
a) 24.2%
b) 18.2%
c) 53.8%
d) none of these.
a) tan (45° - φ)
b) tan (45° + φ)
c) tan2 (45° - φ)
d) none of these
a) directly proportional to the voids ratio
b) inversely proportional to the specific gravity
c) directly proportional to the specific gravity
d) none of these.
a) 80° to 90°C
b) 90° to 95°C
c) 95° to 100°C
d) 105° to 110°C
a) porosity
b) specific gravity
c) void ratio
d) water content.
a) decreases with an increase in the liquid limit
b) increases with an increase in the liquid limit
c) decreases with an increase in the plastic limit
d) is not related with plastic limit.
a) The void space between the soil grains, is filled partly with air and partly with water
b) In perfectly saturated soil, the voids are completely filled with water
c) In dry soil, the voids are completely filled with air
d) all the above.
a) 12 x 10-5 m3/sec
b) 24 x 10-3 m3/sec
c) 6 x 10-5 m3/sec
d) 24 x 10-5 m3/sec
a)

b) 
c)

d) 
a) it can be performed under all three drainage conditions
b) precise measurement of the pore pressure and volume change during the test is possible
c) stress distribution on the failure plane, is uniform
d) all the above.
a) 60%
b) 62%
c) 64%
d) 66%
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
a) free water
b) hydroscopic water
c) gravity water
d) none of these.
a) 0.2200 cm/sec
b) 0.2225 cm/sec
c) 0.2250 cm/sec
d) 0.2275 cm/sec
a) Drain condition cannot be controlled
b) Pore water pressure cannot be measured
c) Shear stress on the failure plane is not uniform.
d) All the above.
a) 4.0 m
b) 12.5 m
c) 25.0 m
d) 15.0 m
a) e = e0 + Cclog10 σ'/σ0'
b) e = e0 - Cclog10 σ'/σ0'
c) e0 = e - Cclog10 σ'/σ0'
d) e0 = e + Cclog10 σ0'/σ'
a) Rankine
b) Coulomb
c) Culaman
d) Mohr.
a) pycnometer
b) oven-drying method
c) calcium carbide method
d) alcohol method.
a) Compaction has no effect on the structure of a soil
b) Permeability decreases with increase in the dry density of a compacted soil
c) A wet side compacted soil is more compressible than a dry side compacted soil
d) None of the these.
a) ultimate load carrying capacity
b) ultimate bearing capacity
c) ultimate bearing resistant
d) all the above.
a) coarse sand
b) fine sand
c) silt
d) clay.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 
a) 90° + effective angle of shearing resistance
b) 90° + half of the angle of shearing resistance
c) 45° - half of the angle of shearing resistance
d) 45° + half of the angle of shearing resistance.
a) expulsion of double layer water from in between the grains
b) sliping of particles to new positions of greater density
c) bending of particles as elastic sheets
d) all the above.
a) positive equipotential lines
b) positive hydrostatic pressure
c) negative hydrostatic pressure
d) none of these.
a) degree of density
b) relativity
c) density index
d) all the above.
a) The property of a soil that enables it to become stiff in a relatively short time on standing is called thixotropy
b) The ratio of shear strength in natural state to the remoulded shear strength under undrained conditions, is called degree of sensitivity.
c) The difference between the undisturbed shear strength and remoulded shear strength is known remoulding loss
d) All the above.
a) 17°C
b) 23°C
c) 27°C
d) 30°
a) Illite bond is weaker than Kaolinite bond
b) Illite bond is stronger than montmorillonite bond
c) Illites are composed of two silica tetrahedralsheets with a central octahedral sheet
d) All the above.
a) 60°C
b) 80°C
c) 100°C
d) 110°C
a) alluvial
b) marine
c) lacustrine
d) loess.
a) liquid state
b) plastic state
c) semi solid state
d) all of these.
a) If the ratio of depth to width is less than 2, it is shallow foundation
b) If the ratio of depth to width is more than 2, it is deep foundation
c) If the ratio of the length to width is between 1 and 2, it is spread foundation
d) All the above.
a) sands
b) clays
c) gravels
d) highly organic soils.
a) 2.65
b) 2.72
c) 2.85
d) 2.90
a) 5 metres
b) 8 metres
c) 10 metres
d) 12 metres
a) The phenomenon of quicksand generally occurs in the cohesionless soil
b) At critical hydraulic gradient, the saturated sand becomes quick
c) The critical gradient depends on the void ratio and the specific gravity
d) All the above.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 
a) show dilatancy
b) swell when moist
c) possess high strength when dry
d) disintegrate easily.
a) quantity of seepage
b) hydrostatic pressure
c) seepage pressure
d) all the above.
a) q times the lateral pressure within the surface
b) 1/q times the lateral pressure within the surface
c) equal to a fill of height Z equal to q/r, where r is the density of the backfill
d) none of these.
a) Isotropic consolidation of clay can be obtained in the triaxial apparatus under equal all-round pressure.
b) If the present effective stress is the maximum to which the clay has ever been subjected, it is called normally consolidated clay
c) If the present effective stress in the past was more than present effective stress, it is called over-consolidated clay
d) All the above.
a) minor principal plane
b) intermediate principal plane
c) major principal plane
d) none of these.
a) 0.002 mm
b) 0.04 mm
c) 0.06 mm
d) 0.08 mm
a) depends upon the force responsible
b) increases as the size of the soil particles increases
c) decreases as the size of the soil particles decreases
d) is less in wet soil than in dry soil.
a) back fill is dry, cohesionless, homogeneous and isotropic
b) slip surface is the plane which passes through the heel of the wall
c) sliding wedge itself acts as a rigid body and the value of earth pressure is obtained by considering the limiting equilibrium of the wedge
d) all the above.
a) 0.375
b) 0.370
c) 0.380
d) 0.390
a) Width of the test pit for plate load test is made five times the width of the plate
b) At the centre of the test pit, a hole is dug out whose size is kept equal to the size of the test plate
c) Bottom level of the hole dug at the centre of the test pit, is kept at the level of the actual formation
d) All the above.
a) soil is homogeneous and isotropic
b) elastic zone has straight boundaries inclined at ψ = φ to the horizontal and plastic zones fully developed
c) failure zones do not extend above the horizontal plane through the base of the footing
d) all the above.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 1 + e/Sr
a) 5
b) 20
c) 40
d) none of these.
a) liquid limit and plastic limit
b) plastic limit and shrinkage limit
c) liquid limit and shrinkage limit
d) none of these.
a) is caused due to relative settlement of the soil
b) is caused in soft clays
c) decreases the pile capacity
d) all of the above.
a) total load on the bearing area
b) safe load on the bearing area
c) load at which soil fails
d) load at which soil consolidates.
a) water
b) glacier
c) gravity
d) all the above.
a) 54%
b) 64%
c) 74%
d) 84%
a) O.M.C. refers to the moisture corresponding to the maximum point on the moisture content dry density curve
b) The line which shows moisture content dry density relation for soil containing a constant percentage of air voids, is known as air void line
c) The weight of hammer used for compaction test is 25 kg
d) All the above.
a) tan (45° - φ)
b) tan (45° + φ)
c) tan2(45° - φ)
d) tan2(45° + φ)
a) Resilience of soils
b) Elasticity of soils
c) Compressibility of soils
d) None of these.
a) 0.91
b) 0.92
c) 0.93
d) 0.95
a) 0.01
b) 0.02
c) 0.05
d) 0.001
a) The smaller the size of the pores, the higher the water can rise above the water table.
b) Below the water table, the pore water may be static.
c) The attractive forces between the particles, caused due to negative pressure of water held above the water table is called soil suction.
d) None of these.
a) liquid limit
b) plastic limit
c) shrinkage limit
d) permeability limit.
a) 1.47
b) 1.82
c) 1.91
d) none of these.
a) 1.6
b) 1.6
c) 2.2
d) 2.6
a) 1.10
b) 1.15
c) 1.20
d) 1.25
a) 2 m
b) 2 m to 3 m
c) 3 m to 4 m
d) 5 m
a) erosion of over burden
b) melting of ice sheets after glaciation
c) permanent rise of water table
d) all the above.
a) homogeneous
b) isotropic
c) incompressible
d) all the above.
a) 
b) 
c) (tan i - tan φ) cos2 i
d) (tan i - tan φ) sin2 i
a) be either straight or curved
b) pass through the origin of stress
c) intersect the shear stress axis
d) all the above.
a) 100 years
b) 120 years
c) 140 years
d) 160 years
a) safe bearing capacity
b) net safe bearing capacity
c) net ultimate bearing capacity
d) ultimate bearing capacity.
a) moisture content
b) compacting content
c) method of compaction
d) All the above.
a) compaction
b) consolidation
c) swelling
d) none of these.
a) particle classification
b) textural classification
c) High Way Research Board classification
d) unified soil classification.
a) 0.5 to 1.0
b) 1.0 to 3.0
c) 3.0 to 4.0
d) 4.0 to 5.0
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 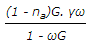
a) 0.55
b) 0.65
c) 0.75
d) 0.80
a) The frictional resistance to translocation between the individual soil particles at their contact point
b) To the structural relation to displacement of the soil because of the interlocking of the particles
c) Cohesion and adhesion between the surfaces of the soil particles
d) All the above.